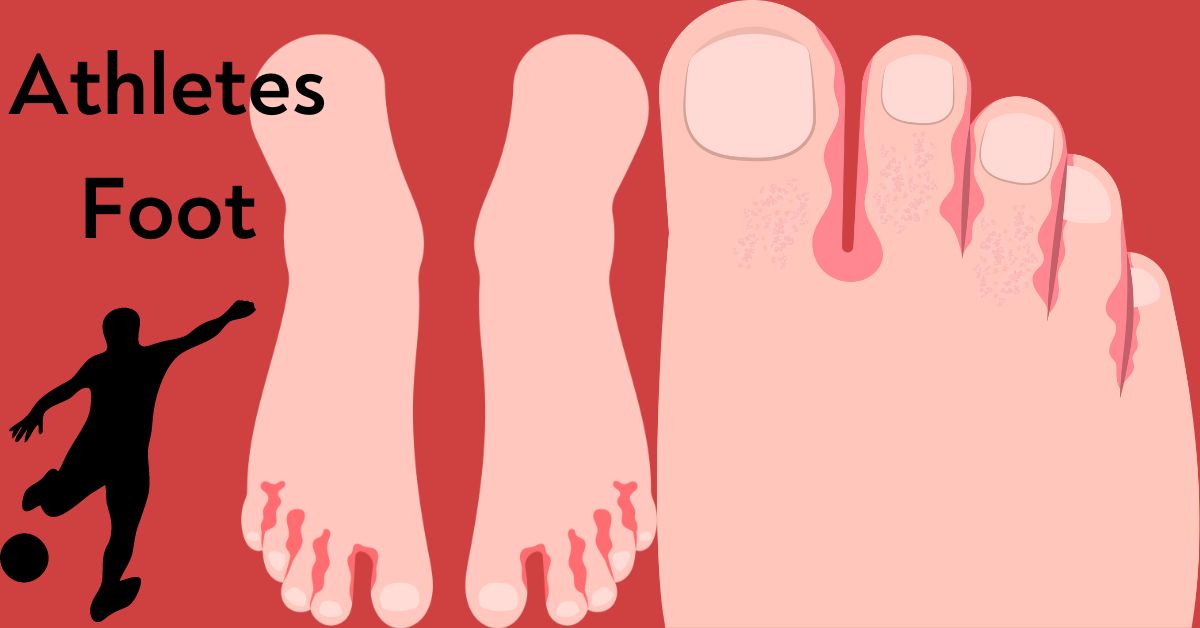
Athlete’s foot, restoratively known as tinea pedis, is a parasitic contamination that commonly influences the skin between the toes and on the soles of the feet. It is caused by different sorts of organisms, basically having a place to the dermatophyte bunch. This condition is exceedingly infectious and frequently spreads in warm, wet situations such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and showers where individuals walk unshod.
What Causes Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot flourishes in warm, sodden situations, such as sweat-soaked shoes or soggy socks. It spreads through coordinate contact with an tainted individual or backhanded contact with surfaces sullied with the organisms. Components that increment the hazard of creating athlete’s foot include:
Wearing tight, closed-toe shoes: These make a warm, muggy environment perfect for parasitic growth.
Frequenting clammy open places: Such as locker rooms, swimming pools, and communal showers where parasites can thrive.
Sweating intensely: Intemperate sweating can make conditions conducive to contagious infections.
Compromised resistant framework: People with debilitated safe frameworks are more susceptible.
Not keeping feet dry: Destitute foot cleanliness can contribute to parasitic growth.
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot
- Itching and burning: Particularly between the toes and on the soles of the feet.
- Cracked, rankled, or peeling skin: Frequently went with by redness and inflammation.
- Dryness and scaling: Skin may ended up dry and flaky, with scaling in a few cases.
- Blisters and ulcers: Extreme cases may lead to rankling or ulcers, which can be painful.
Diagnosing Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is regularly analyzed based on the appearance of the skin and side effects portrayed by the understanding. In a few cases, a specialist may rub off a little test of the influenced skin for examination beneath a magnifying lens or for parasitic culture to affirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for athlete’s foot ordinarily includes antifungal drugs, which can be connected topically or taken orally, depending on the seriousness of the infection:
Topical antifungals: Creams, treatments, or showers are viable for mellow to direct contaminations. They are connected specifically to the influenced skin and ought to be utilized as coordinated until indications resolve.
Oral antifungals: Medicine medicines may be fundamental for serious or diligent contaminations that do not react to topical medications alone. These medicines are taken by mouth and work systemically to dispense with the fungi.
In expansion to medicine, it is imperative to hone great foot cleanliness and take preventive measures to dodge reinfection or spreading the contamination to others.
Prevention Tips
Preventing athlete’s foot includes decreasing presentation to the parasites and minimizing conditions that advance its growth:
Keep feet clean and dry: Wash feet every day with cleanser and water, and dry them altogether, particularly between the toes.
Wear moisture-wicking socks: Select socks made of characteristic or manufactured filaments that draw dampness absent from the skin.
Use antifungal powders or splashes: Particularly in shoes that tend to trap moisture.
Alternate shoes: Permit shoes to discuss out and dry totally between wearings, particularly athletic shoes and boots.
Avoid strolling unshod: Particularly in open places like locker rooms, showers, and swimming pools.
Choose well-ventilated footwear: Pick for shoes made of breathable materials that permit discuss circulation around the feet.
Key Takeaways
- Itching: Often extreme and persistent, particularly between the feet.
- Redness and scaling: Skin may seem purple, cracked, or scaly.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled blisters can form on the inflamed pores and skin.
- Odor: Fungal infections can motive ugly foot smell.
Effective remedy includes antifungal medicinal drugs, both topical and oral, depending at the severity of the infection. Preventive measures encompass keeping toes easy and dry, carrying breathable socks and shoes, and warding off strolling barefoot in public areas.
Advantages of Treatment
- Symptom alleviation: Itching and pain reduce appreciably.
- Prevents unfold: Prompt treatment prevents the infection from spreading to different components of the frame or to others.
- Faster recovery: Skin heals faster with appropriate antifungal medicinal drugs.
- Prevents complications: Avoids potential complications consisting of secondary bacterial infections.
Disadvantages of Untreated Athlete’s Foot
- Spread of infection: It can spread to different elements of the body just like the arms or groin.
- Chronic soreness: Persistent itching and pain can affect daily life.
- Secondary infections: Increases the hazard of bacterial infections inside the affected area.
- Longer healing: Delayed treatment may require longer and extra intensive therapy.
Table: Comparison of Athlete’s Foot Treatments
| Treatment Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical antifungals | Creams, sprays applied directly to affected areas | Easy application, effective for mild cases | May require extended use for severe infections |
| Oral antifungals | Tablets or capsules taken by mouth | Effective for severe infections | Potential side effects (e.g., liver toxicity) |
| Home remedies | Vinegar soaks, tea tree oil | Natural, low cost | Limited scientific evidence |
| Prevention measures | Keeping feet dry, wearing breathable footwear | Effective in preventing recurrence | Requires consistent practice |
FAQS About Athletes foot
What causes athlete’s foot?
Athlete’s foot is caused by parasitic contaminations, especially dermatophytes, which flourish in warm, wet environments.
How is athlete’s foot diagnosed?
Diagnosis is ordinarily based on indications and physical examination. In a few cases, a skin scratching may be inspected beneath a magnifying lens or refined to affirm the nearness of fungi.
What are the chance variables for athlete’s foot
Risk variables incorporate strolling unshod in open regions, wearing tight or non-breathable shoes, sharing towels or footwear with contaminated people, and having a debilitated safe system.
Can athlete’s foot spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, if cleared out untreated, the contamination can spread to other regions like the hands (tinea manuum) or the crotch (tinea cruris).
How can athlete’s foot be prevented?
Prevention incorporates keeping feet clean and dry, wearing moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes, dodging strolling unshod in open ranges, and not sharing towels or footwear with others.
Conclusion
Athlete’s foot is a common parasitic disease that influences numerous people around the world. Whereas it can cause distress and burden, provoke treatment with antifungal medicines and preventive measures can viably oversee and decrease the chance of repeat. By understanding its indications, treatment alternatives, and preventive methodologies, people can way better secure themselves and others from this infectious condition. Early intercession not as it were lightens side effects but too anticipates potential complications, guaranteeing a faster return to consolation and ordinary day by day exercises.